Updated: January 24, 2024 - 13 min read
Are you looking to elevate your career and navigate the forefront of technological innovation? How prepared are you to lead the evolution of product management and successfully transition into an AI/ML PM? This post focuses on staying current with industry trends and emphasizes the crucial step of evolving from a traditional PM to an AI/ML PM. Undertaking this transition could be a defining move in the trajectory of your professional growth.
Editorial note: This post is based on a talk by Chinmaya Madan, Microsoft Product Leader, on Launching a Career as an AI/ML PM and contains additional insights and examples from the Product School team. You can watch the webinar in full above.
In this post, you can expect to find:
Core PM Skills Refresher: Starting with essential skills every PM must have, reinforcing the foundation of a successful product professional.
Understanding AI/ML in Product Management: Exploring AI/ML's role and impact, key to transforming product development and strategy.
AI/ML PM Skills: Examining the specific skills needed for AI/ML product management, how they differ from traditional PM roles, and the additional knowledge required.
AI/ML PM Responsibilities: Discussing the unique duties of an AI/ML Product Manager.
How to be a good PM first
To start an AI/ML PM career, first get strong basic PM skills. Then, build on them with specialized knowledge like ML techniques and data science. These advanced skills are valuable enhancements, but they should always uphold the core attributes of a proficient PM.
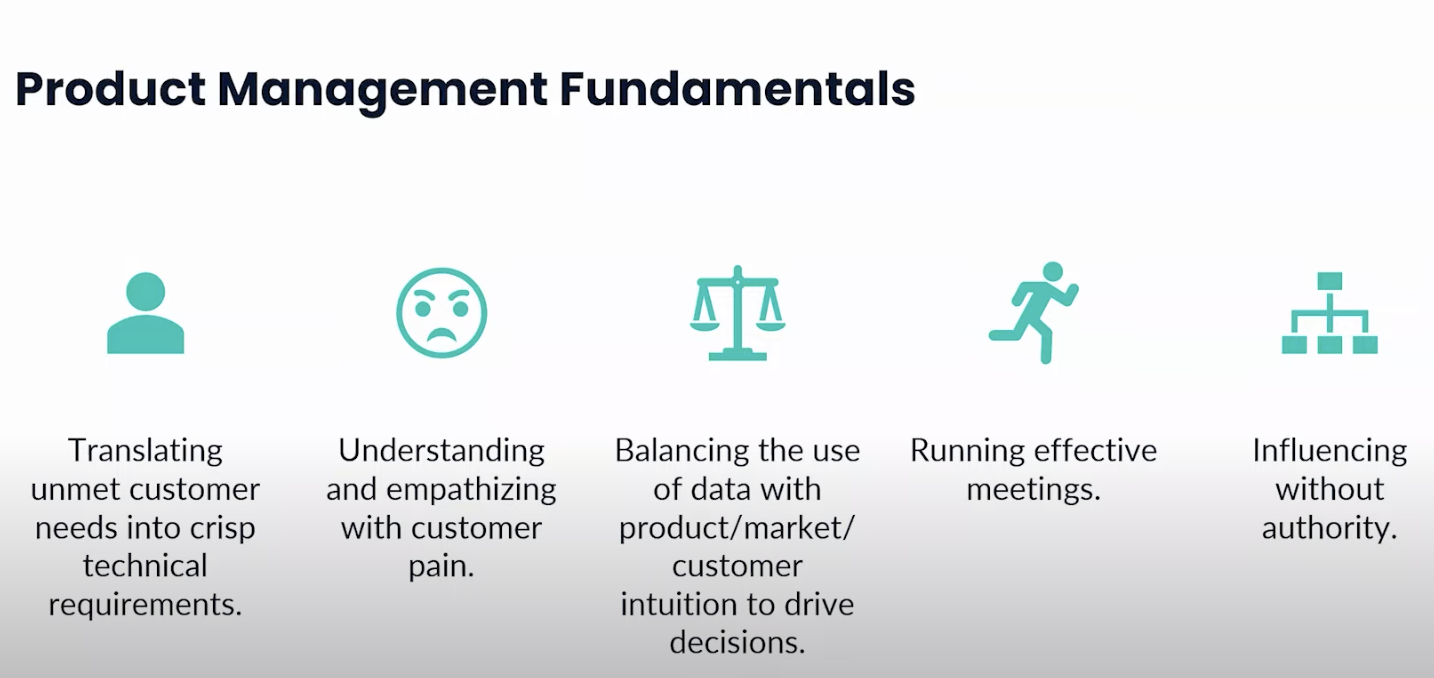
1. Customer centricity
The hallmark of a successful PM lies in an unwavering customer obsession. It's about deeply understanding and empathizing with your customer's needs and preferences. Your role as a PM pivots on this customer-centric approach, guiding product development to ensure the end product truly resonates with its intended audience.
2. Translating needs into requirements
Your ability to convert customer needs into precise technical requirements is key. It bridges the gap between customer expectations and what your product delivers.
3. Communication mastery
Effective communication, both verbal and written, is non-negotiable. You're often the liaison between diverse stakeholders. Needing to explain complex ideas clearly and simply.
4. Empathetic problem-solving
Understanding customer pain points goes beyond mere acknowledgment. It's about identifying genuine problems and distinguishing them from less critical 'nice-to-haves.'
5. Data-intuition balance
The best PMs master the art of balancing data-driven insights with customer intuition, especially vital in product marketing.
6. Effective meeting management
Running efficient, goal-oriented meetings is a skill often overlooked but vital for productive collaboration.
7. Influencing without authority
Your ability to influence without direct authority is crucial. This is even more pertinent in AI/ML, where stakeholder diversity is vast.
Discover the Product Manager Certification (PMC)™
Learn everything you need to succeed as a Product Manager. From getting your first job to crushing it during your first 90 days (and beyond), the Product Manager Certification will set you up for success.
Find out More
Where does AI sit in Product Management?
The role of AI
The current technological revolution is focused on developing intelligent products and features. We've moved beyond the iterative process of releasing new gadgets to embedding intelligence in these devices. This intelligence is about predicting user needs and tailoring software responses in real time, which is where true innovation lies.
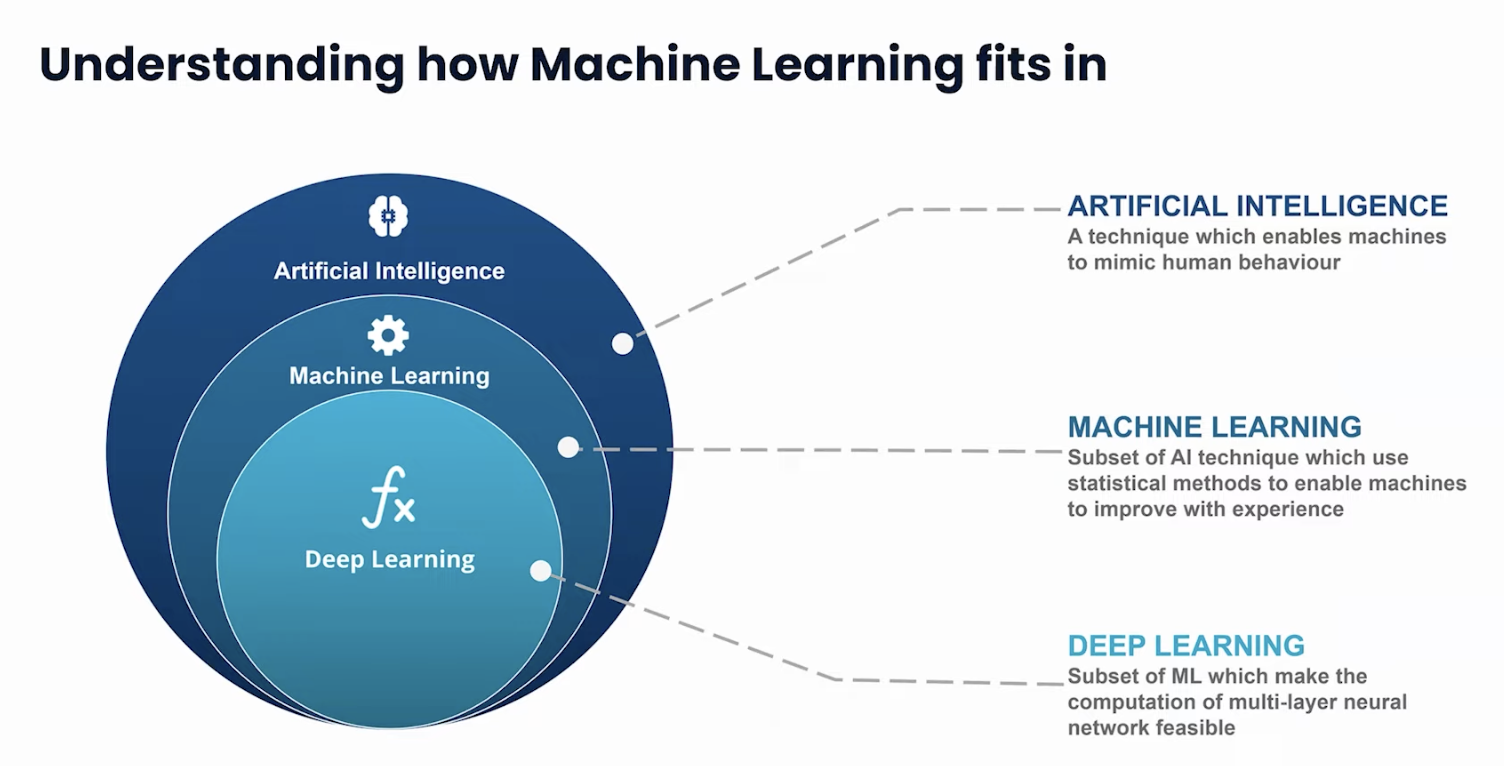
AI encompasses the ability of machines to emulate human behavior. This includes Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), our current state, where machines perform specific tasks, and Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), a futuristic notion where machines make autonomous decisions - think "I, Robot".
ML, a subset of ANI, employs statistical methods to enable machines to learn from experience. This often involves structured data, like the data in Excel spreadsheets or databases, as opposed to unstructured data, such as audio, video, and text, which don't fit into traditional data structures.
Learn more about how to become an ML PM
Dive into ML products and explore how these stand out. Learn all you need to know about Machine Learning development.
Read more
Deep learning, a branch of ML, is particularly intriguing due to its connection with neural networks. Deep learning plays a crucial role in processing unstructured data, like classifying images or text - consider the simple yet effective "hot dog or not hot dog" classifier.
The key takeaway is the role of AI, through ML and deep learning, in driving technological advancement by making products smarter and more attuned to user needs.
ML product development life cycle
It's essential to understand the life cycle that underpins the creation of AI-driven products. This AI life cycle comprises several stages, each playing a vital role in ensuring the success of the product.
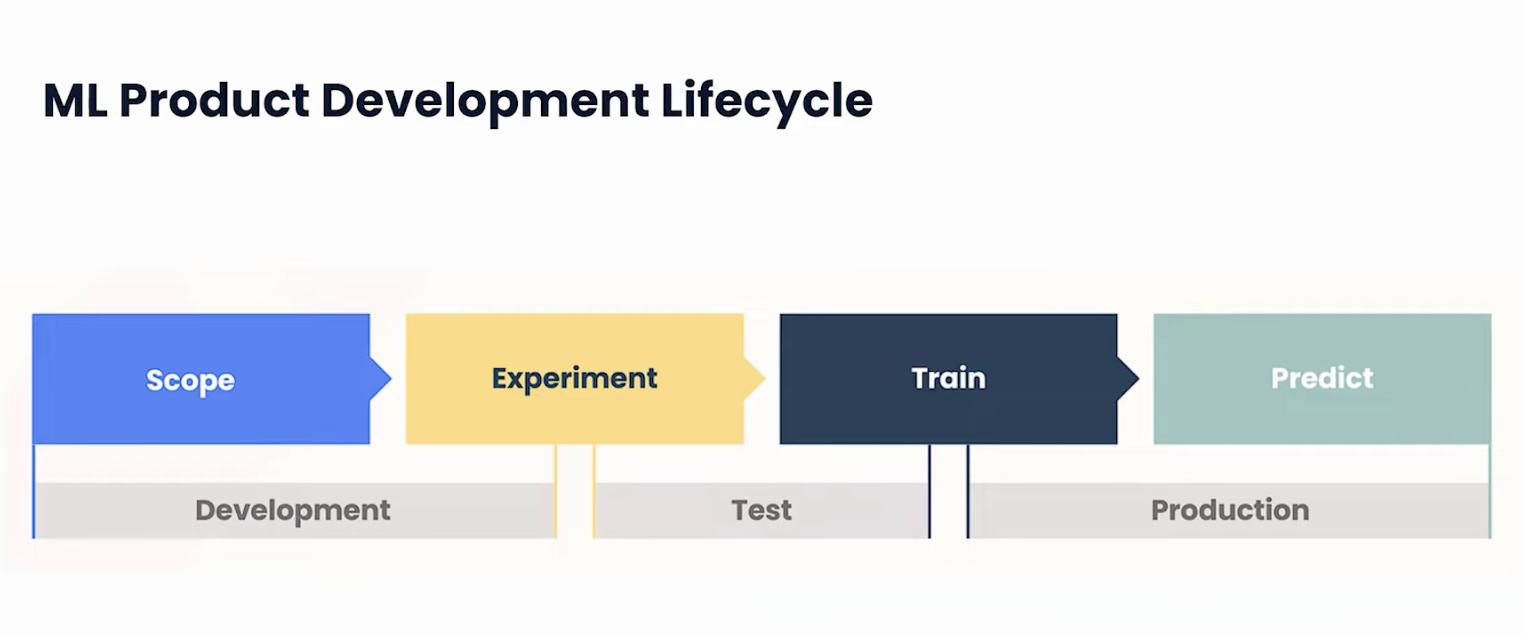
1. Scoping
Your team collaborates to deeply understand the challenges and intricacies of the AI product's vision. It's a stage where you assess the problems at hand and strategize effectively to allocate the resources and efforts needed for the project.
2. Experimentation
Similar to traditional product development, this stage involves building a prototype or a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). However, in ML development, there's a twist. It's not just about creating a functional product; your team must wisely choose a mathematical model and approach that best leverages the available data to deliver promising outcomes.
3. Training
Instead of creating new models from scratch, the focus here is on utilizing pre-trained models and shaping the data to suit these models effectively. Your goal is to refine the data in a way that extracts the best possible results from these models.
4. Serving
The model is put to the test in a real-world environment, facing the ultimate test with actual data. The outcomes can go two ways: the model performs as expected, mirroring the confidence level seen during training, or it falls short, sending you back to the drawing board to adjust and realign.
Feedback loop in AI/ML
Overall, to transition into an AI/ML PM, you’ll need a deep understanding of the AI/ML product development process we’ve just explained. Central to this understanding is the CRISP-DM framework, a guide for modern data analysts, data scientists, and AI/ML product managers. In AI projects, the feedback loop is a feature of the development process and an integral part of the AI products themselves.
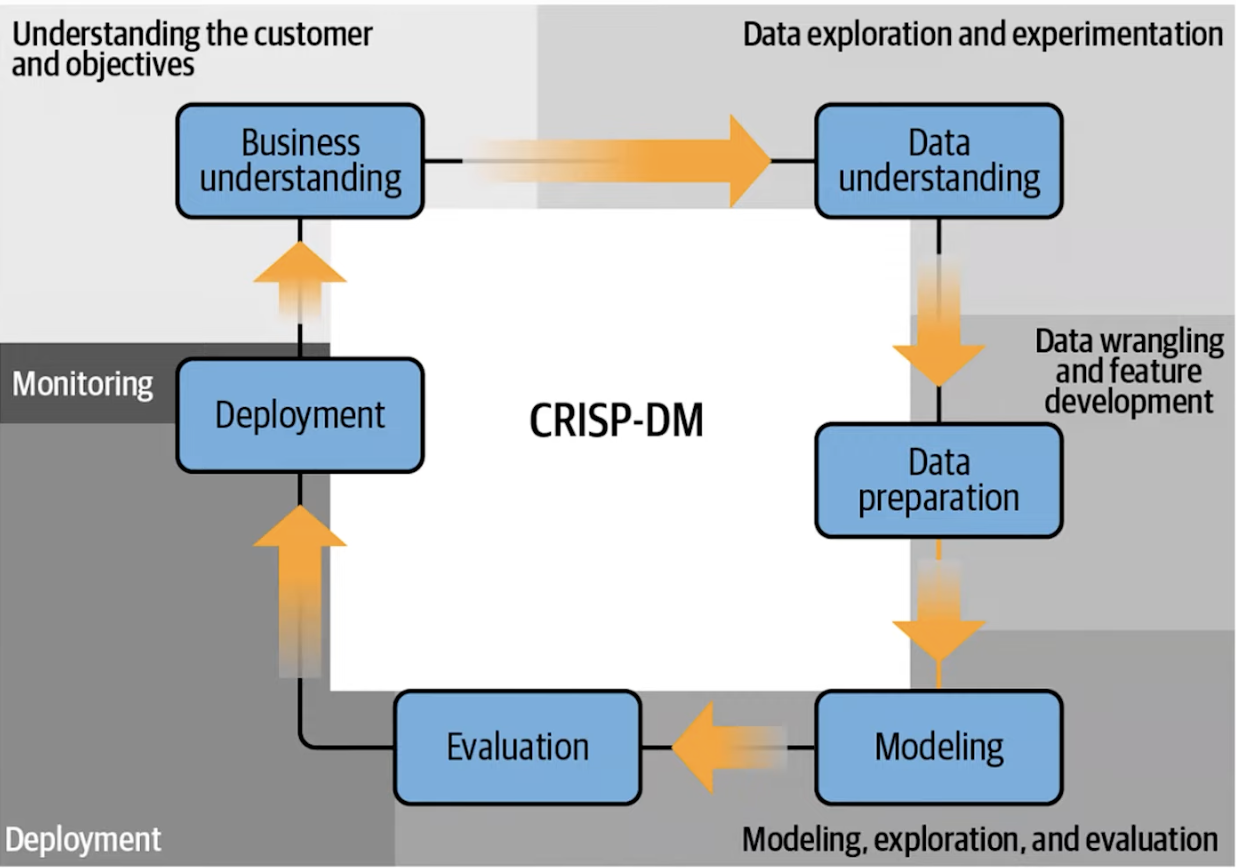
1. Experimentation and iterative development
AI-driven products are inherently based on research, making experimentation and iterative development a MUST. This marks a shift from traditional software development's deterministic approach to a probabilistic one in AI, where outcomes are not always certain. This uncertainty demands significant adaptations in how projects are set up and executed.
2. Data understanding and acquisition
A substantial segment of the AI/ML product lifecycle is dedicated to understanding data. Successfully navigating this phase is often an indicator of the project's future success.
As an AI/ML PM, you must balance resource investment against the potential risks of moving forward without a comprehensive understanding of the available data. Data acquisition poses its own set of challenges, especially in regulated industries.
3. Guiding the research process
Your role is pivotal in leading data scientists, analysts, and domain experts to evaluate data with a product-centric lens. The objective is to ensure that the data at hand is not only measurable but also provides meaningful insights and directs feature design effectively.
4. Data wrangling and feature engineering
Data wrangling and feature engineering are both critical and challenging aspects of AI projects. With data scientists dedicating a significant portion of their time to feature engineering, the importance of these phases cannot be overstated. Despite advancements in AutoML and deep learning reducing time and effort, developing a superior feature pipeline or model architecture is still key.
1. Modeling phase
The modeling phase involves an iterative cycle between understanding data and modeling to align outcomes with user needs.
It's a crucial stage where data insights are continuously integrated into the modeling process to ensure that the final model accurately reflects and responds to what users actually need and want. This phase is vital for tailoring AI/ML products to deliver relevant and effective solutions.
2. Involvement in the build process
Traditional DevOps processes, tailored for conventional software, don't fully cater to the needs of ML/AI products, necessitating a more custom approach to the skills and tools used in AI/ML product management.
3. Monitoring and adaptation
The real-world data may not always align with the predictions made during training, necessitating continuous monitoring and adaptation. Setting up alerts for deviations and working closely with site reliability teams or engineers ensures the model remains accurate and relevant.
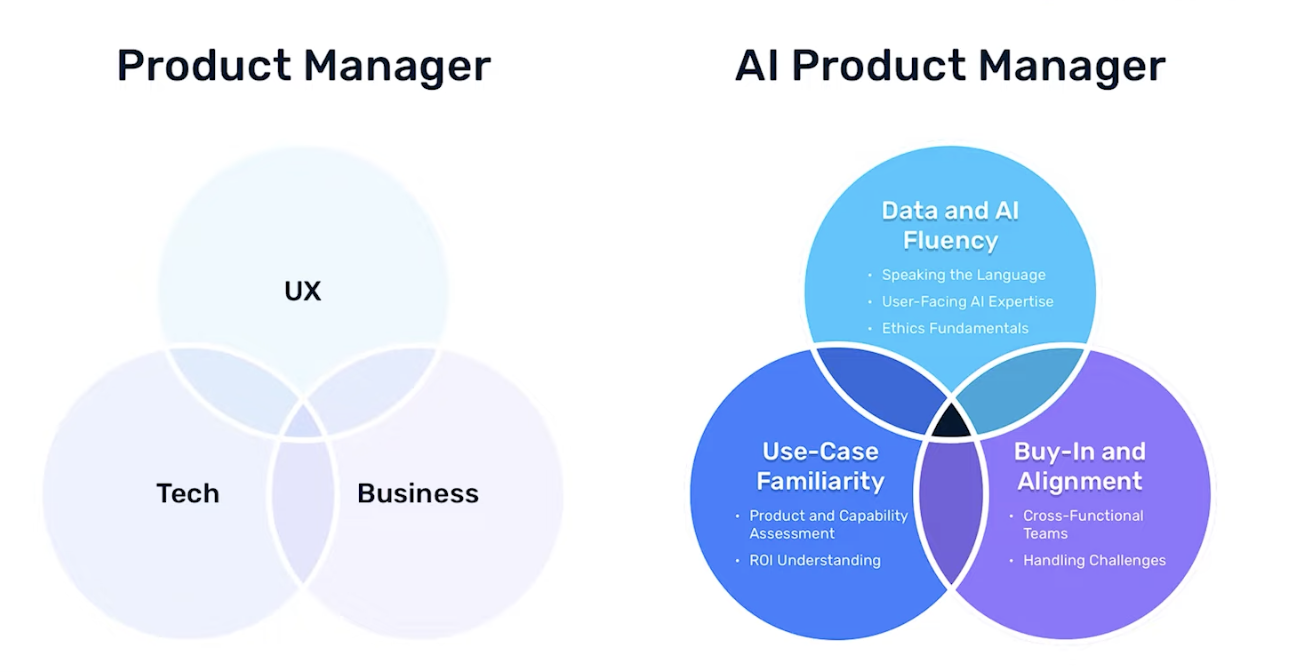
What skills do you need to build an AI/ML PM career?
How do you translate your current knowledge and experience into the specific competencies needed for AI/ML product management? Recognizing and acquiring the right set of skills is key to your success.
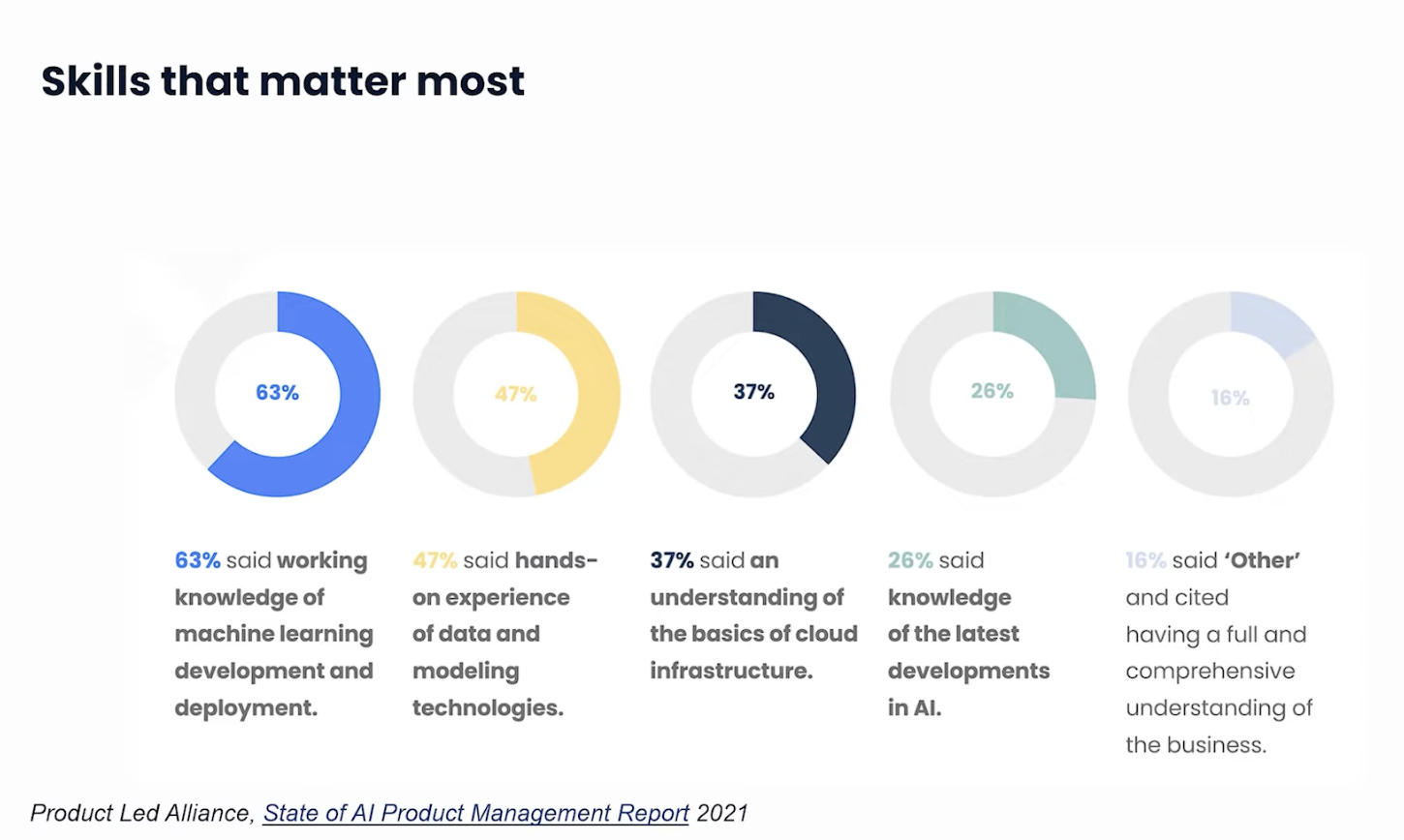
1. Integrating ML in your products
The ability to effectively integrate ML into products is a rare and in-demand skill. This skill is not merely technical but is fundamentally rooted in innovative product development. Your role here is about understanding the technology and how it can transform the product to provide a unique and enhanced user experience.
2. Gaining a practical understanding
Gaining a hands-on understanding of ML includes the entire spectrum of building a model from scratch to achieving predictive results and understanding the nuances in between. As an AI/ML PM, your role is less about building the models and more about being the knowledgeable authority on their functionality.
3. Exploring ML systems
Understanding systems' intricacies and their integration into products is a key component of an AI/ML product manager's skill set. Let's look at some ML systems that are integral to many of today's products:
Recommender and ranking Systems: These systems, like those used in streaming services or e-commerce platforms, personalize the user experience by suggesting relevant items.
Event or action prediction models: Used for predicting user actions, such as Google predicting which videos you are likely to click on.
Classification models: These models are widely used for categorizing data, such as filtering spam emails.
4. Actioning results: integration path
How and where will the model's predictions be displayed? How do you turn these outcomes into actionable results for users? Whether it’s enhancing existing features, enabling new features, or creating new products, understanding the integration path is paramount.
Enhancing existing features: Refining a recommendation system to align more closely with user preferences.
Enabling new features: For example, Google's reverse image search represents a leap in search technology.
Creating new products: For instance, developing enterprise tools that provide insights into organizational patterns and trends.
Responsibilities and challenges of an AI/ML PM
Your role is a unique blend of technical mastery, strategic foresight, and coordination across various teams. Let's dive into what it means to be an AI/ML PM and the key responsibilities and challenges that come with this role.
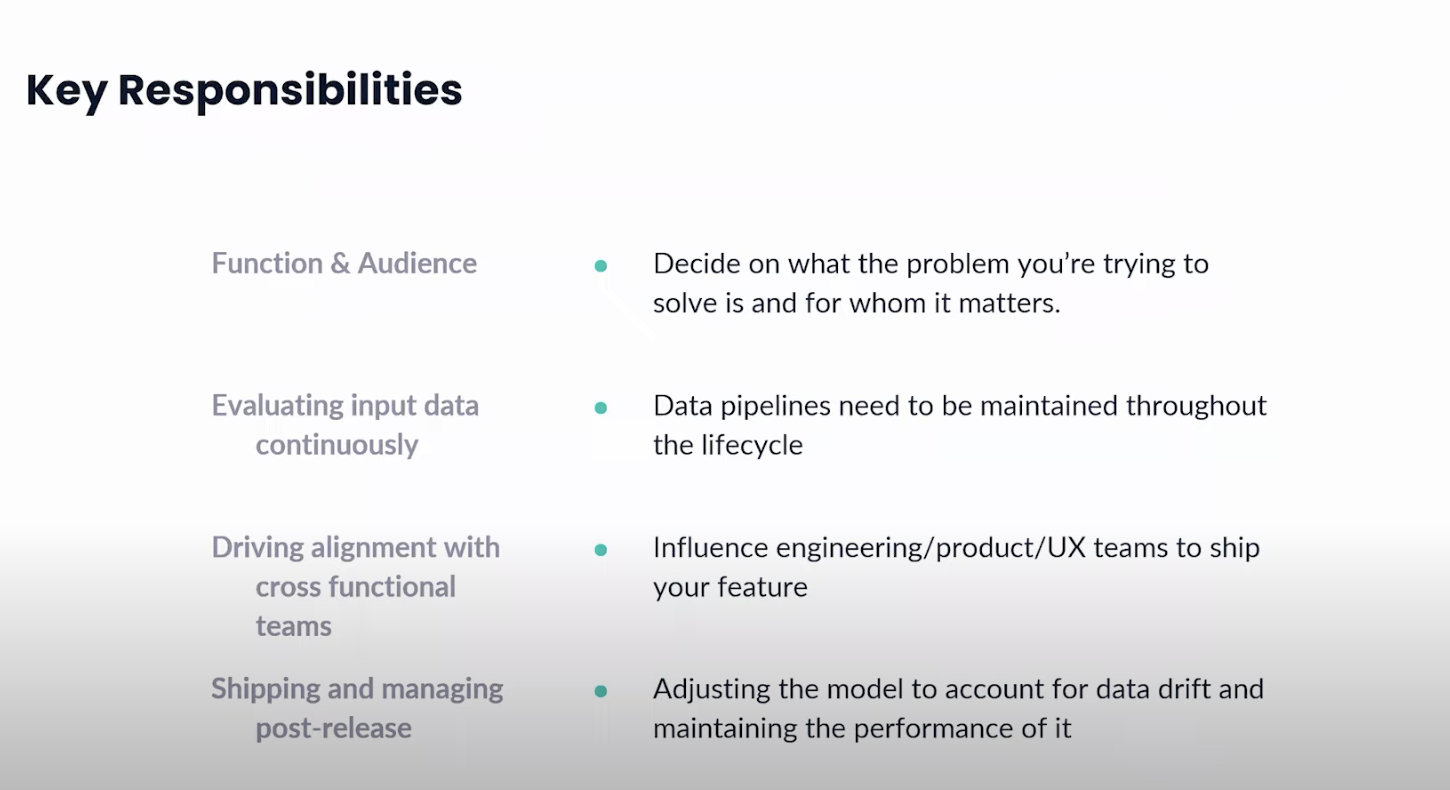
What matters most
The essence of your role in AI/ML lies in bridging the gap between data science and product development. You're not just delivering AI-powered specifications to your data science team; you're also a linchpin in solving and prioritizing user-centric problems. The technical nature of AI/ML demands clear and concise communication to ensure all stakeholders are on the same page.
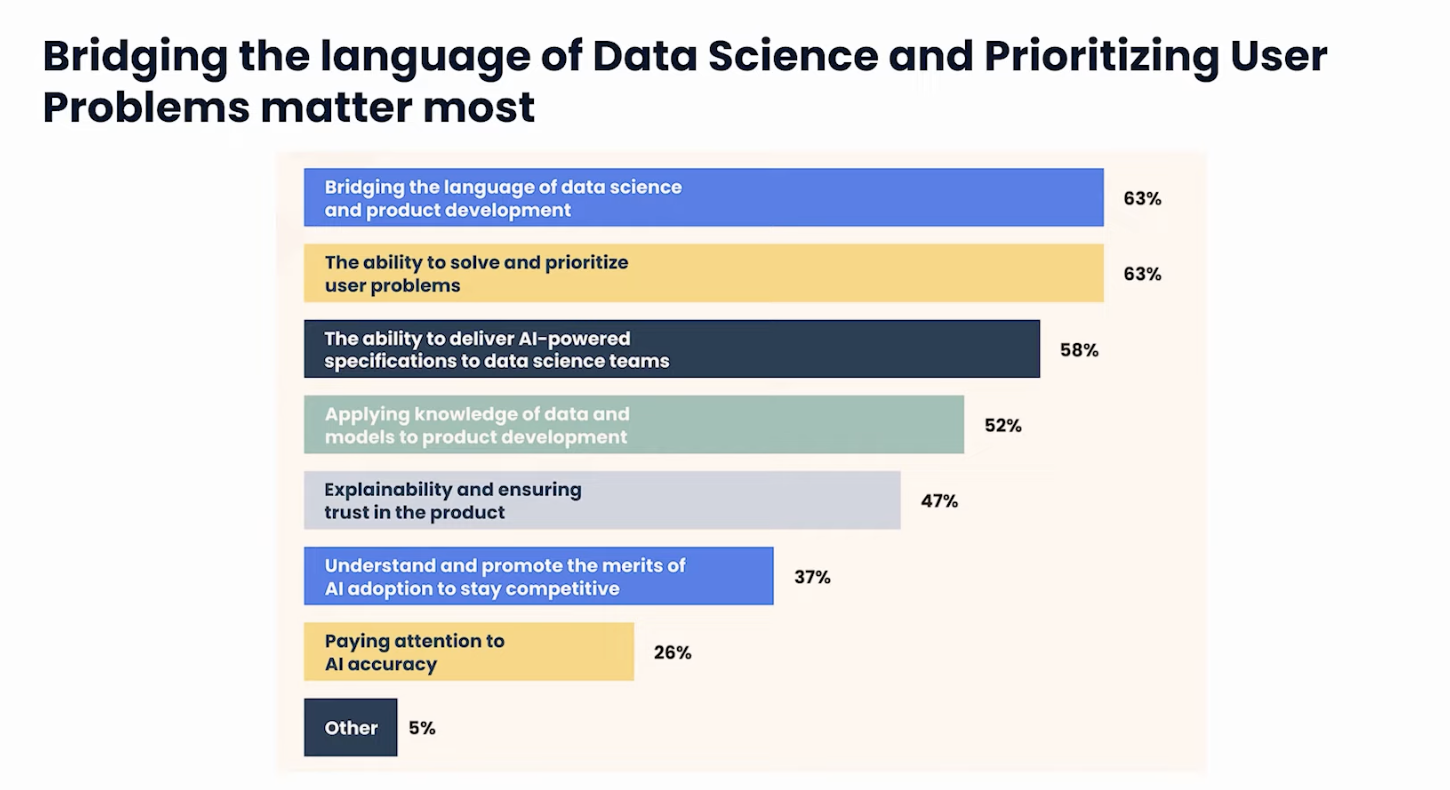
Key responsibilities of an AI/ML PM
Problem identification: Your primary task is to identify the core problem your AI/ML product aims to solve and understand its impact on your target audience.
Data pipeline management: Overseeing the data pipelines is crucial. You ensure their efficiency and maintenance throughout the product's lifecycle, which is essential for the smooth operation of AI models.
Leading cross-functional teams: You'll be at the helm, coordinating with teams across data engineering, research science, data science, ML engineering, and software engineering.
Interface and design decisions: A significant part of your role involves making key decisions about user interfaces and designing the user experience, particularly in the context of feature engineering.
Model integration: Integrating the AI/ML model with existing software architectures and ensuring seamless operation is a critical technical responsibility.
Collaboration on tech stack: Working alongside ML engineers and data scientists, you'll contribute to the design and decision-making process of the technical stack.
Product shipping and management: Post-release, your job entails managing the product's performance, making necessary adjustments, and overseeing its overall success.
Coordination with engineering teams: Ensuring scalability and support for all shipped features by collaborating with engineering, infrastructure, and site reliability teams is another key responsibility.
Common challenges as an AI/ML PM
Poor data quality and availability: Despite data abundance, the quality and availability of data remain a significant challenge. The data collected through legacy systems often doesn't align with the needs of modern AI/ML systems.
Data collection and cleaning: As an AI/ML PM, you're responsible for ensuring that the data collected is as clean and relevant as possible. This means not just collecting data for the sake of it but focusing on gathering data that adds value to your product.
Addressing data-related challenges: This includes evaluating data sources for quality and relevance, implementing data cleaning processes, and developing a strategic data collection approach. Collaborating with data engineers and scientists is essential to align these practices with the broader goals of AI/ML development.
Preparing for an AI/ML PM interview
As you set your sights on a role in AI/ML product management, you may wonder how best to prepare for the interview. This preparation is key. Let’s break down the key areas you should focus on to ace your AI/ML PM interview.
1. Product sense
This involves a deep understanding of the product's core purpose, its target audience, and its position in the market. But it goes beyond just understanding - it's about anticipating. Can you foresee user needs and preferences? How well can you tailor your product's features and functionalities to meet these expectations?
This ability is a cornerstone in demonstrating your proficiency as a product manager, especially in the AI/ML space where user needs can be complex and ever-evolving.
2. Proficiency in statistics
When stepping into AI/ML product management, your acumen in statistics needs to be top-notch. This isn't just a cursory knowledge of basic stats but a deep dive into p-values, confidence intervals, hypothesis testing, and sampling techniques.
Your interview might delve into these areas, assessing your ability to interpret data and make data-driven decisions. The key here is to blend intuition with statistical knowledge, allowing you to navigate through vast data sets and extract meaningful insights.
3. Setting success metrics
In an AI/ML PM career, success metrics take on a new level of importance. You're expected to not only understand but also articulate the impact of a model's output in a real-world production environment.
This is where frameworks like MECE (Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive) come into play. They help you structure your thinking process, enabling you to solve problems and make decisions effectively.
Mapping user actions to metrics and contextualizing why these metrics are significant is an essential skill. It's about connecting the dots – how user behavior impacts product performance and, in turn, the overall business objectives.
Pro tip: The interview preparation strategy
As you prepare for your AI/ML PM interview, it's important to build a strong foundation in the areas above. Demonstrating strength in these competencies shows that you're not just technically adept but also possess the strategic thinking and decision-making skills crucial for success in this field.
An AI/ML PM interview is not just a test of your technical knowledge but also an assessment of how you apply this knowledge strategically to real-world scenarios. Your ability to blend technical know-how with practical product management skills will set you apart as a candidate poised for success in the exciting world of AI and ML product management.
Updated: January 24, 2024